

| CS 535: Object-Oriented Programming & Design |
|---|
| ...Repetitive Strain Injuries | slide # 1 |
| ...Arrays | slide # 2 |
| ......Multidimensional Arrays | slide # 6 |
| ...Strings | slide # 7 |
| ......Reading Command Line Arguments | slide # 12 |
| ...Control Structures | slide # 15 |
| ......Methods | slide # 19 |
Repetitive Strain Injury: A Computer User's Guide
by Emil Pascarelli, MD
& Deborah Quilter
John Wiley & Sons, Inc
1994
Cost $14.95 in 1994
You can order directly from Wiley at:
1-800-225-5945
class ArrayExamples {
public static void main( String args[ ] ) {
int declarationTypeA[ ] = new int[5];
float[ ] floatArray;
int[] factorial = { 1, 1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720, 5040 };
char[] vowels = { 'a', 'e', 'o', 'i', 'u' };
floatArray = new float[ 25 ];
// indexing starts at zero
System.out.println( vowels[ 0 ] );
System.out.println( floatArray.length );
floatArray[ 32] = 42;
System.out.println( "Never Reach here, " +
"Array bounds are checked at runtime" );
}
}
class ArraysAreReferences {
public static void main( String args[ ] ) {
int[ ] integerArray ;
int[ ] alias;
integerArray = new int[ 4 ];
for ( int index = 0; index < integerArray.length; index++
)
integerArray[ index ] = 5;
alias = integerArray; // Arrays are references
alias[ 2 ] = 4
System.out.println( integerArray[ 2 ] );
integerArray = new int[ 3 ];
System.out.println( integerArray[ 2 ] );
System.out.println( alias[ 2 ] );
System.out.println( integerArray );
alias = new int[5];
}
}
Output





class ArrayExamples
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int[] integerArray = new int[ 4 ];
integerArray[ 1 ] = 12
integerArray = new int[ 2 ]; // Memory Leak - No!
integerArray[ 1 ] = 5;
int[] aliasForArray = integerArray;
aliasForArray[ 1 ] = 10;
System.out.println( integerArray[ 1 ] ); //Prints 10
}
}
class MultidimensionalArrayExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int[][] squareArray = new int [ 10 ] [ 20 ];
squareArray[ 2 ] [ 5 ] = 25;
int[][][] threeDArray = new int [ 10 ] [ 20 ][ 5 ];
int[][] oddShaped;
oddShaped = new int [ 4 ] [ ] ;
oddShaped [ 0 ] = new int [ 5 ];
oddShaped [ 1 ] = new int [ 2 ];
oddShaped [ 2 ] = new int [ 6 ];
oddShaped [ 3 ] = new int [ 3 ];
for ( int row = 0; row < oddShaped.length; row ++ )
for ( int col = 0; col < oddShaped[ row ].length; col++
)
oddShaped[ row ][ col ] = 10;
}
}

class StringExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
String firstName = " Roger ";
String lastName = " Whitney ";
String fullName = firstName + lastName;
System.out.println( fullName );
firstName = firstName.toLowerCase();
lastName = lastName.toUpperCase();
System.out.println( firstName );
firstName = firstName.trim(); // trim leading, trailing
lastName = lastName.trim(); // white space
lastName = lastName.replace( 'I', 'a' );
System.out.println( firstName + lastName );
String floatAsString = String.valueOf( 13.4e+5f);
System.out.println( floatAsString );
}
}
Roger Whitney
roger
rogerWHaTNEY
1.34e+06
class StringConstantExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
String firstName = "ROGER";
firstName.toLowerCase();
System.out.println( firstName );
firstName = firstName.toLowerCase();
System.out.println( firstName );
}
}
public class StringTest
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
String me = "Roger";
if ( me == "Roger" )
System.out.println( "Yes, I am me" );
else
System.out.println( "No, I am not me?" );
String shortName = me.substring( 0, 3 );
System.out.println( shortName );
if ( shortName == "Rog" )
System.out.println( "Very Good" );
else
System.out.println( "Trouble here" );
if ( shortName.equals( "Rog" ) )
System.out.println( "Do it this way" );
}
}String variables are references
The == operator check to see if two string references refer to the same memory location
if ( me == "Roger" )
System.out.println( "Yes, I am me" );
else
System.out.println( "No, I am not me?" );
Compilers are allowed, but not required to store equal strings in the same memory location.
The compiler can not always store equal strings in the same memory location
Be safe and use the "equals" method to compare strings
| charAt(int) | replace(char,char) |
| compareTo(String) | startsWith(String) |
| concat(String) | substring(int,int) |
| copyValueOf(char[]) | toCharArray() |
| endsWith(String) | toLowerCase() |
| equals(Object) | toUpperCase() |
| equalsIgnoreCase(String) | trim() |
| getChars(int,int,char[],int) | valueOf(int) |
| indexOf(String) | valueOf(long) |
| lastIndexOf(String) | valueOf(float) |
| length() | valueOf(double) |
| regionMatches(int,String,int,int) |
class CommandLineExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
System.out.println( args.length );
for ( int k = 0; k < args.length; k++ )
{
System.out.println( "Argument " + k + "\t" + args[ k ] );
};
}
}
Example of Running Programrohan 16-> java CommandLineExample a b c d e 5 Argument 0 a Argument 1 b Argument 2 c Argument 3 d Argument 4 e
class CommandLineProperty
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
String firstName = System.getProperty( "first" );
String defaultLastName = "Missing";
String lastName = System.getProperty( "last",
defaultLastName );
System.out.println( firstName );
System.out.println( lastName );
}
}
Sample Use of Programeli-> java -cs -Dfirst=Roger -Dlast=Whitney CommandLineProperty Roger Whitney eli-> java -cs -Dfirst=Roger CommandLineProperty Roger Missing eli-> java -cs CommandLineProperty -Dfirst=Roger null Missing
import sdsu.util.LabeledData;
class CommandLineFlags
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
LabeledData flags = new LabeledData();
flags.fromCommandLine( args );
String userFirstName;
if ( flags.containsKey( "first" ) )
userFirstName = flags.getData( "first" );
else
userFirstName = "Not Known";
String userLastName =
flags.getData( "last", "Not Known");
System.out.println( userFirstName );
System.out.println( userLastName );
}
}eli-> java CommandLineFlags -first Roger Roger Not Known eli-> java CommandLineFlags -first=Roger Roger Not Known eli-> java CommandLineFlags -last=Whitney Not Known Whitney
class Control
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int a = 5;
int b = 10;
if ( a > b ) System.out.println( "a is bigger ");
if ( a > b )
System.out.println( "a is bigger ");
else
System.out.println( "b is bigger ");
switch ( a )
{ //Controlling expression converted to int
case 4:
b++;
break;
case 10:
b--;
break;
default: // optional
System.out.println( "Default action" );
};
// Control Structures Continued
while ( a < b )
{
a++;
};
for ( int loop = 0; loop < a; loop++ )
{
System.out.println( a );
};
System.out.println( loop ); // Error, loop does not
// exist here
do
{
System.out.println( a-- );
System.out.println( b );
}
while ( a > b );
int max = ( a > b ) ? a : b;
if ( ( a > 5 ) && ( b < 10 ) )
System.out.println( "Good" );
a += ( a = 5 ); // What does this do?
}
}
class ControlStructures
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
for ( int row = 0; row < 5; row++ )
{
for ( int column = 0; column < 4 ; column++ )
{
System.out.println( row + "\t" + column );
if ( ((row + column) % 2 ) == 0 )
break;
System.out.println( " After if " );
}
};
}
}
Outputclass ControlStructures
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
Outer:
for ( int row = 0; row < 5; row++ )
{
for ( int column = 0; column < 4; column++ )
{
System.out.println( row + "\t" + column );
if ( ((row + column) % 2 ) == 0 )
break Outer;
System.out.println( " After if " );
}
}
}
}class SampleFunction
{
public static int subtractOne( int decreaseMe )
{
return decreaseMe - 1;
}
public static void main( String[] args )
{
int startValue = 5;
int smaller = subtractOne( startValue );
int larger = addOne( startValue );
System.out.println( "smaller = " + smaller + "\n" +
"larger = " + larger );
}
public static int addOne( int increaseMe )
{
return increaseMe + 1;
}
}In the last example the methods, subtractOne and addOne, should not be static
After we have covered classes I will not accept this use of static.
Once we have covered classes it should be very clear why
this use of static is not to be tolerated
class TestParameter
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
int startValue = 5;
noChange( startValue );
System.out.println( startValue );
}
public static void noChange( int fixed )
{
fixed = fixed + 10;
}
}
class ArrayAsParameter
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int[] integerArray = new int[ 3 ];
integerArray[ 1 ] = 5;
modifyElements( integerArray, 9 );
System.out.println( integerArray[ 1 ] );
}
public static void modifyElements( int[] changeMe,
int newValue )
{
for ( int index = 0; index < changeMe.length; index++
)
changeMe[ index ] = newValue;
}
}
integerArray[ 1 ] = 5;in modifyElements modifyElements( integerArray, 9 );
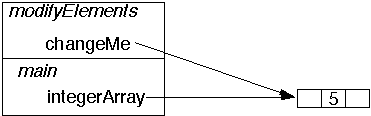
for ( int index = 0; index < changeMe.length; index++ )
changeMe[ index ] = newValue;

class ArrayAsParameter
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int[] integerArray = new int[ 3 ];
integerArray[ 1 ] = 5;
doesNotWork( integerArray );
System.out.println( integerArray[ 1 ] );
}
public static void doesNotWork( int[] changeMe )
{
changeMe = new int[ 3 ];
for ( int index = 0; index < changeMe.length; index++
)
changeMe[ index ] = 999;
}
}
In main
integerArray[ 1 ] = 5;


