 CS 696: Advanced OO
CS 696: Advanced OODoc 14 Composite and Decorator
 CS 696: Advanced OO
CS 696: Advanced OO
| Composite | slide # 1 |
| ...Example - Motivation | slide # 1 |
| ...Issue: WidgetContainer Operations | slide # 6 |
| ...Explicit Parent References | slide # 7 |
| ...Applicability | slide # 8 |
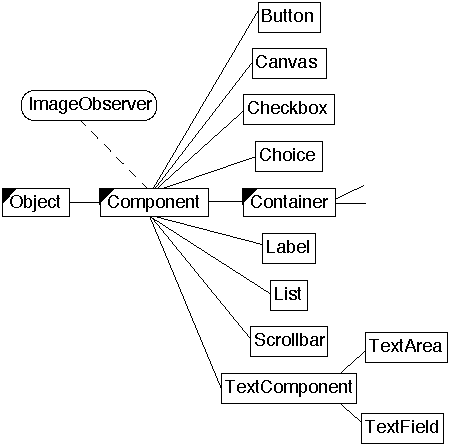
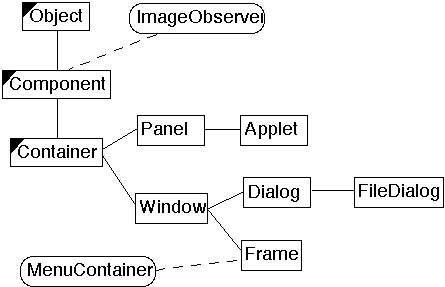
| ...Java Use of Composite - AWT Widgets | slide # 9 |
| Decorator | slide # 11 |
| ...Solution 1 - Use Strategy | slide # 12 |
| ...Solution 2 - Use Decorator | slide # 13 |
| ...Applicability | slide # 15 |
| ...Consequences | slide # 15 |
| ...Implementation Issues | slide # 16 |
| ...Java Example of Decorator - Streams | slide # 17 |
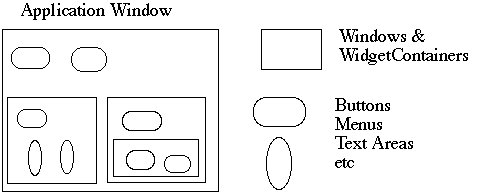
How does the window hold and deal with the different items it has to manage?
Widgets are different that WidgetContainers
class Window
{
Buttons[] myButtons;
Menus[] myMenus;
TextAreas[] myTextAreas;
WidgetContainer[] myContainers;
public void update()
{
if ( myButtons != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myButtons.length(); k++ )
myButtons[k].refresh();
if ( myMenus != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myMenus.length(); k++ )
myMenus[k].display();
if ( myTextAreas != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myButtons.length(); k++ )
myTextAreas[k].refresh();
if ( myContainers != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myContainers.length(); k++ )
myContainers[k].updateElements();
etc.
}
public void fooOperation()
{
if ( blah ) etc.
if ( blah ) etc.
}
}
A Better Idea - Program to an interface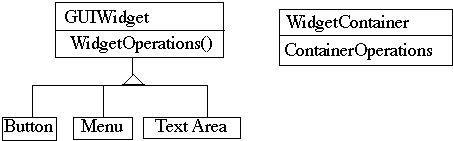
class Window
{
GUIWidgets[] myWidgets;
WidgetContainer[] myContainers;
public void update()
{
if ( myWidgets != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myWidgets.length(); k++ )
myWidgets[k].update();
if ( myContainers != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myContainers.length(); k++ )
myContainers[k].updateElements();
etc.
}
}
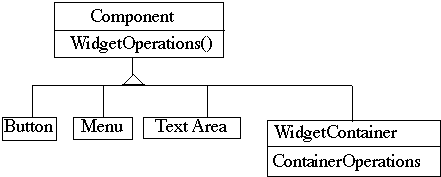
Component implements default behavior for widgets when possible
Button, Menu, etc overrides Component methods when needed
WidgetContainer will have to overrides all widgetOperations
class WidgetContainer
{
Component[] myComponents;
public void update()
{
if ( myComponents != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myComponents.length(); k++ )
myComponents[k].update();
}
}Should the WidgetContainer operations be declared in Component?
All subclasses can be treated alike. (?)
Declaring them in WidgetContainer is safer
Adding or removing widgets to non-WidgetContainers is an error
What should be the proper response to added a TextArea to a button? throw an exception?
One out is to check the type of the object before using a WidgetContainer operation
class WidgetContainer
{
Component[] myComponents;
public void update()
{
if ( myComponents != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myComponents.length(); k++ )
myComponents[k].update();
}
public add( Component aComponent )
{
myComponents.append( aComponent );
aComponent.setParent( this );
}
}
class Button extends Component
{
private Component parent;
public void setParent( Component myParent)
{
parent = myParent;
}
etc.
}
Who should delete components -
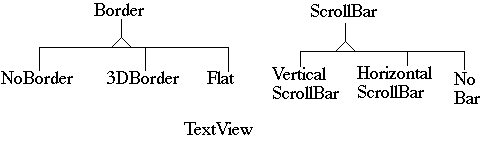
A text view has the following features:
class TextView
{
Border myBorder;
ScrollBar verticalBar;
ScrollBar horizontalBar;
public void draw()
{
myBorder.draw();
verticalBar.draw();
horizontalBar.draw();
code to draw self
}
etc.
}
But TextView know about all the variations!
TextView has no borders or scrollbars!
Add borders and scrollbars on top of a TextView
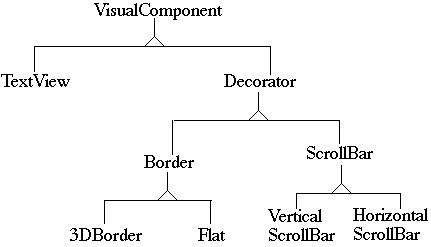
class TextView
{
public void draw()
{
code to draw self
}
etc.
}class FlatBorder
{
VisualComponent myComponent;
public FlatBorder( VisualComponent aComponent )
{
myComponent = aComponent
}
public void draw()
{
int width = myComponent.width();
int height = myComponent.height();
myComponent.draw();
code to draw FlatBorder
}
}
main()
{
TextView taxSummary = new TextView();
VisualComponent flatTax = new FlatBorder( taxSummary );
VisualComponent longTax = new VerticalScrollBar( flatTax );
now use longTax
}
Avoids feature laden classes
Lots of little classes
A decorator and its components are not identical
Don't put data members in VisualComponent

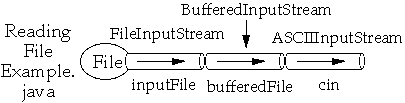
import java.io.*;
import sdsu.io.*;
class ReadingFileExample
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception
{
FileInputStream inputFile;
BufferedInputStream bufferedFile;
ASCIIInputStream cin;
inputFile = new FileInputStream( "ReadingFileExample.java" );
bufferedFile = new BufferedInputStream( inputFile );
cin = new ASCIIInputStream( bufferedFile );
System.out.println( cin.readWord() );
for ( int k = 1 ; k < 4; k++ )
System.out.println( cin.readLine() );
}
}