 CS 696: Advanced OO
CS 696: Advanced OODoc 21, Flyweight and Adapter
 CS 696: Advanced OO
CS 696: Advanced OO
| Flyweight | slide # 1 |
| Adapter | slide # 4 |
| ...The Adridecoxegate Pattern? | slide # 7 |
The pattern can be used when all the following are true
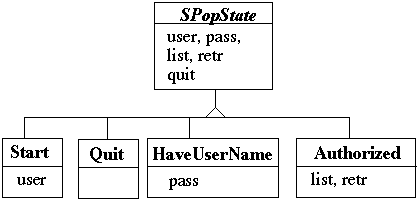
State transitions
Start state comes first
When get user name transfer to HaveUserName state
When get correct password transfer to Authorized state
HaveUserName and Authorized states need the user name
In concurrent server we may have many (100's ) different users connected at the same time.
State creation can become expensive, so create each state once (Singleton pattern)
Each time use the state pass the user name to the state
class HaveUserName extends SPopState
{
private HaveUserName() {};
private static HaveUserName instance;
public getInstance( )
{
if ( instance == null )
instance = new HaveUserName();
return instance;
}
public SPopState pass( String userName, String password )
{
if ( validateUser( userName, password )
return Authorized.getInstance();
else
return Start.getInstance();
}
}
Use the Adapter pattern when you want to use an
existing class and its interface does not match the one
you need
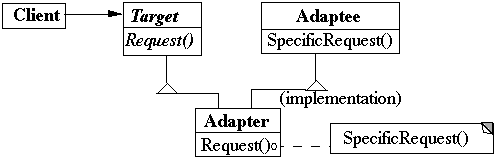
Class Adapter Example
class OldSquarePeg
{
public:
void squarePegOperation()
{ do something }
}
class RoundPeg
{
public:
void virtual roundPegOperation = 0;
}
class PegAdapter: private OldSquarePeg, public RoundPeg
{
public:
void virtual roundPegOperation()
{
add some corners;
squarePegOperation();
}
}
void clientMethod()
{
RoundPeg* aPeg = new PegAdapter();
aPeg->roundPegOperation();
}
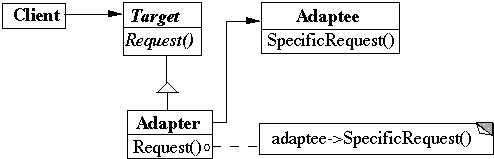
class OldSquarePeg {
public:
void squarePegOperation() { do something }
}
class RoundPeg {
public:
void virtual roundPegOperation = 0;
}
class PegAdapter: public RoundPeg {
private:
OldSquarePeg* square;
public:
PegAdapter() { square = new OldSquarePeg; }
void virtual roundPegOperation() {
add some corners;
square->squarePegOperation();
}
}
This makes the details differ
Adapter uses an old class in a new situation
Changes the interface of an existing object
Bridge separates an interface from its implementation so that they can vary easily and independently
Decorator adds functionality to another object without changing its interface
Proxy just controls access to an object
Strategy encapsulates an algorithm
State encapsulates state dependent behavior