
Fall Semester, 2000
Polymorphism
© 2000, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney
San Diego State University -- This page last updated 05-Sep-00

|
CS 535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design Fall Semester, 2000 Polymorphism |
|
|---|---|---|
|
© 2000, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney San Diego State University -- This page last updated 05-Sep-00 |
Polymorphism
Java Inheritance Example public class Parent{ public void foo() { System.out.println( "Parent foo" ); bar(); } public void bar(){ System.out.println( "Parent bar" ); } } public class ChildFoo extends Parent{ public void foo(){ System.out.println( "ChildFoo foo" ); bar(); } } public class ChildBar extends Parent{ public void bar(){ System.out.println( "ChildBar bar" ); } }What is the Output Here? public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent test = new Parent(); test.foo(); test = new ChildFoo(); test.foo(); test = new ChildBar(); test.foo(); } }
Java Interface Example public interface Parent{ public void foo(); public void bar(); } public class ChildFoo implements Parent{ public void foo(){ System.out.println( "ChildFoo foo" ); bar(); } public void bar(){ System.out.println( "ChildFoo bar" ); } } public class ChildBar implements Parent{ public void foo(){ System.out.println( "ChildBar foo" ); bar(); } public void bar(){ System.out.println( "ChildBar bar" ); } }What is the Output Here? public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) { Parent test = new ChildFoo(); test.foo(); test = new ChildBar(); test.foo(); } }
Polymorphism and C++
See http://www.eli.sdsu.edu/courses/fall95/cs596_1/notes/Poly/Poly.html for a more complete example of polymorphism and C++
#include <iostream.h> class Parent { public: void virtual foo(); void virtual bar(); }; void Parent::foo() { cout << "Parent foo" << endl; bar(); } void Parent::bar() { cout << "Parent bar" << endl; } class ChildFoo : public Parent { void virtual foo(); }; void ChildFoo::foo() { cout << "ChildFoo foo" << endl; bar(); } class ChildBar : public Parent { void virtual bar(); }; void ChildBar::bar() { cout << "ChildBar bar" << endl; }
Virtual + Pointers
int main() { Parent* test = new Parent; test->foo(); test = new ChildFoo; test->foo(); test = new ChildBar; test->foo(); }Output Parent foo Parent bar ChildFoo foo Parent bar Parent foo ChildBar bar
Just Virtual int main() { Parent test; test.foo(); ChildFoo child; test = child; test.foo(); }
Output Parent foo Parent bar Parent foo Parent bar
C++ without Virtual Functions #include <iostream.h> class Parent { public: void foo(); void bar(); }; void Parent::foo() { cout << "Parent foo" << endl; bar(); } void Parent::bar() { cout << "Parent bar" << endl; } class ChildFoo : public Parent { public: void virtual foo(); }; void ChildFoo::foo() { cout << "ChildFoo foo" << endl; bar(); } class ChildBar : public Parent { void virtual bar(); }; void ChildBar::bar() { cout << "ChildBar bar" << endl; }
Pointers but not Virtual
int main() { Parent* test = new Parent; test->foo(); test = new ChildFoo; test->foo(); test = new ChildBar; test->foo(); ChildFoo child; child.foo(); }Output Parent foo Parent bar Parent foo Parent bar Parent foo Parent bar ChildFoo foo Parent bar
Simplistic Example
Last Federal Virtual Bank wants its entire banking software redone in Java, so it can shut down its branch offices and perform all its business via the WWW.
Customer records include the customers name, address, personal information, passwords, etc. and accounts.
The bank offers various types of accounts: checking, savings, CD, Junior savings accounts.
Bank officers will introduce new types of accounts from time to time.
Checking account charge 12 cents/check unless the average account balance for the month is greater than $1,000. The first three ATM transactions per month are free. Additional ATM transactions cost 50 cents.
All transactions over $1,000 dollars must be reported to the federal government.
Junior savings accounts are for children under the age of 13. Children can deposit any amount into the account. Deposits of over $100 are reported to their parents. Children can withdrawal up to $10 from the account. Individual withdrawals over $10 must be verified by a parent. Total withdrawals over $100 per month are reported to the parents.
Transactions include time & date, amount, location, type of transaction, account number and teller.
Banking Classes
Customer
Transaction
Currency
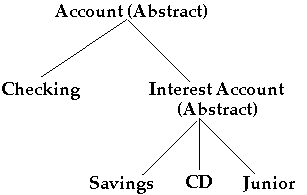
Account
abstract class account { public static final boolean VALID = true; protected Customer accountOwner; protected Currency balance; protected Stack accountHistory; // Other fields left out public void processTransaction( Transaction accountActivity ) { if ( validateTransaction( accountActivity ) == VALID ) commitTransaction( accountActivity ); else // report the problem. Code not shown } protected abstract boolean validateTransaction( Transaction accountActivity ); protected abstract void commitTransaction( Transaction accountActivity ); // other methods left out }
Account Class Inheritance
Polymorphism
Account newCustomer; newCustomer = magicFunctionToCreateNewAccount() newCustomer.processTransaction( amount );Which processTransaction is called?
Adding new types of accounts to program requires:
Modular Design Rule

Avoid Case (and if) Statements
switch ( newCustomer.accountType ) { case SAVINGS: // Code to process Savings account case CD: // Code to process CD account case CHECKING: // Code to process Checking account // etc. }
newCustomer.processTransaction( amount );
|
|