 CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
Fall Semester, 1996
Doc 21, AWT Basics
[To Lecture Notes Index]
San Diego State University -- This page last updated Nov 11, 1996

Contents of Doc 21, AWT Basics
- References
- Building GUIs - Abstract Window Toolkit (AWT)
- Overview and Basics
- Events
- Graphics
- Drawing
- Fonts
- Cursors
Core Java, Chapter 6
Graphic Java, Geary and McClellan, Chapters 3, 4
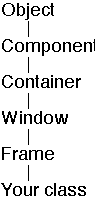
 Types of things in AWT
Types of things in AWT
Components
- Basic UI things like
- Buttons, Checkboxes, Choices,
- Lists, Menus, and Text Fields
- Scrollbars and Labels
Containers
- Contain components and containers
- Window
Layouts
- Position items in window
Graphics
- Drawing on the screen
Graphics 101
Window Coordinate System

First Example
import java.awt.*;
class HelloApplication extends Frame
{
public void paint( Graphics display )
{
int startX = 30;
int startY = 40;
display.drawString( "Hello World", startX, startY );
}
}
class Test
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
HelloApplication mainWindow = new HelloApplication();
int HorizontalPixelSize = 150;
int VerticalPixelSize = 80;
mainWindow.resize( HorizontalPixelSize, VerticalPixelSize );
mainWindow.show();
}
}

Subclass Frame to get a window
Paint is called when window needs to be drawn
Becareful! It is hard to exit from this program
Hello Again
import java.awt.*;
class Hello extends Frame
{
public Hello( int width, int height, String title )
{
resize( width, height );
setTitle( title );
show();
}
public void paint( Graphics display )
{
int startX = 30;
int startY = 40;
display.drawString( "Hello World", startX, startY );
}
}
class Test
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
Hello mainWindow = new Hello( 150, 80, "Hi Dad");
}
}
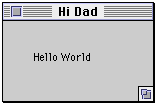
Quitting (already?)
import java.awt.*;
class HelloApplication extends Frame
{
public HelloApplication( int widthInPixels, int heightInPixels )
{
setTitle( "Hi Mom" );
resize( widthInPixels, heightInPixels );
}
public boolean handleEvent( Event userAction )
{
if ( userAction.id == Event.WINDOW_DESTROY )
{
System.exit(0);
return true; // return true if you handle the event
}
else
return super.handleEvent( userAction );
// When you don't handle the event
}
public void paint( Graphics display )
{
int startX = 30;
int startY = 40;
display.drawString( "Hello World", startX, startY );
}
public static void main( String args[] )
{
HelloApplication mainWindow;
mainWindow = new HelloApplication( 300, 200 );
mainWindow.show();
}
}
Result of Running Program

When the user does something that affects a window, an event is sent to the
window
Types of things a user can do:
- mouse click
- type a key
- move mouse
- drag mouse
- move windows
- resize windows
- press buttons
- scroll a window
- close windows
An event object contains:
-
- target
- the part of the window the event is meant for
- when
- the time stamp of when the event occurred
- id
- which type of event occurred
- x
- y
- the x and y coordinate of a mouse event
- key
- the key pressed in a keyboard event
- modifiers
- the state of the modifier keys
- arg
- general purpose object for transferring information
What Events are There?
Window Events
| WINDOW_DEICONIFY | WINDOW_ICONIFY |
| WINDOW_DESTROY | WINDOW_MOVED |
| WINDOW_EXPOSE | |
Keyboard Events
| KEY_ACTION | KEY_PRESS |
| KEY_ACTION_RELEASE | KEY_RELEASE |
Mouse Events
| MOUSE_DOWN | MOUSE_EXIT |
| MOUSE_DRAG | MOUSE_MOVE |
| MOUSE_ENTER | MOUSE_UP |
Scrollbar Events
| SCROLL_ABSOLUTE | SCROLL_PAGE_DOWN |
| SCROLL_LINE_DOWN | SCROLL_PAGE_UP |
| SCROLL_LINE_UP | |
List Events
Action Events
| ACTION_EVENT | LOST_FOCUS |
| GOT_FOCUS | SAVE_FILE |
| LOAD_FILE | |
How to show events
import java.awt.*;
class ShowEvents extends Frame
{
String eventType = " ";
public ShowEvents( int WidthInPixels, int heightInPixels )
{
setTitle( "Show Events" );
resize( WidthInPixels, heightInPixels );
}
public boolean handleEvent( Event userAction )
{
if ( userAction.id == Event.WINDOW_DESTROY )
displayMessage( "WINDOW_DESTROY" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.MOUSE_DOWN )
displayMessage( "MOUSE_DOWN" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.MOUSE_ENTER )
displayMessage( "MOUSE_ENTER" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.MOUSE_EXIT )
displayMessage( "MOUSE_EXIT" );
return super.handleEvent( userAction );
}
public void displayMessage( String message)
{
System.out.println( message );
eventType = message;
repaint(); // redraw the window
}
public void paint( Graphics display )
{
display.drawString( eventType , 30, 40 );
}
public static void main( String args[] ){
ShowEvents mainWindow = new ShowEvents( 300, 200 );
mainWindow.show();
}
}
Output

Comments
To redraw the screen, call repaint()
repaint will call paint
Do not call paint directly
System.out.println( message ) was called for debugging
and to show history, not normally done
public void displayMessage( String message)
{
System.out.println( message );
eventType = message;
repaint(); // redraw the window
}
Showing All Events
The following program will show all events that are sent to the window
You will not be able to generate all events at this time!
Have fun
import java.awt.*;
class ShowEvents extends Frame
{
String eventType = " ";
public ShowEvents( int WidthInPixels, int heightInPixels )
{
setTitle( "Show All Events" );
resize( WidthInPixels, heightInPixels );
}
public boolean handleEvent( Event userAction )
{
if ( userAction.id == Event.ACTION_EVENT )
displayMessage( "ACTION_EVENT" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.DOWN )
displayMessage( "DOWN" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.GOT_FOCUS )
displayMessage( "GOT_FOCUS" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.KEY_ACTION )
displayMessage( "KEY_ACTION" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.KEY_ACTION_RELEASE )
displayMessage( "KEY_ACTION_RELEASE" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.KEY_PRESS )
displayMessage( "KEY_PRESS" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.KEY_RELEASE )
displayMessage( "KEY_RELEASE" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.LEFT )
displayMessage( "LEFT" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.LIST_DESELECT )
displayMessage( "LIST_DESELECT" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.LIST_SELECT )
displayMessage( "LIST_SELECT" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.LOAD_FILE )
displayMessage( "LOAD_FILE" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.LOST_FOCUS )
displayMessage( "LOST_FOCUS" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.MOUSE_DOWN )
displayMessage( "MOUSE_DOWN" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.MOUSE_DRAG )
displayMessage( "MOUSE_DRAG" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.MOUSE_ENTER )
displayMessage( "MOUSE_ENTER" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.MOUSE_EXIT )
displayMessage( "MOUSE_EXIT" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.MOUSE_MOVE )
displayMessage( "MOUSE_MOVE" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.MOUSE_UP )
displayMessage( "MOUSE_UP" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.SAVE_FILE )
displayMessage( "SAVE_FILE" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.SCROLL_ABSOLUTE )
displayMessage( "SCROLL_ABSOLUTE" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.SCROLL_LINE_DOWN )
displayMessage( "SCROLL_LINE_DOWN" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.SCROLL_LINE_UP )
displayMessage( "SCROLL_LINE_UP" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.SCROLL_PAGE_DOWN )
displayMessage( "SCROLL_PAGE_DOWN" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.SCROLL_PAGE_UP )
displayMessage( "SCROLL_PAGE_UP" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.WINDOW_DEICONIFY )
displayMessage( "WINDOW_DEICONIFY" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.WINDOW_DESTROY )
displayMessage( "WINDOW_DESTROY" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.WINDOW_EXPOSE )
displayMessage( "WINDOW_EXPOSE" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.WINDOW_ICONIFY )
displayMessage( "WINDOW_ICONIFY" );
else if ( userAction.id == Event.WINDOW_MOVED )
displayMessage( "WINDOW_MOVED" );
return super.handleEvent( userAction );
}
public void displayMessage( String message)
{
System.out.println( message );
eventType = message;
repaint(); // redraw the window
}
public void paint( Graphics display )
{
display.drawString( eventType , 30, 40 );
}
public static void main( String args[] ){
ShowEvents mainWindow = new ShowEvents( 300, 200 );
mainWindow.show();
}
}
Handling Events
There are three different ways in which a window can be notified of events
1) handleEvent
- Window has a handleEvent method which is sent all events
-
- The handleEvent picks the events it is interested in them and handles the
event
2) Special convenience methods handle a specific event
| action( Event, Object ) | mouseEnter( Event, x, y ) |
| keyDown( Event, int key ) | mouseExit( Event, x, y ) |
| keyUp( Event, int key ) | mouseMove( Event, x, y ) |
| mouseDown( Event, x, y ) | mouseUp( Event, x, y ) |
| mouseDrag( Event, x, y ) | |
3) Button and menu can handle events
Using Convenience Event Methods
import java.awt.*;
class EventMethods extends Frame {
String eventMessage = " ";
public EventMethods( int WidthInPixels, int heightInPixels ) {
setTitle( "Event Methods" );
resize( WidthInPixels, heightInPixels );
show();
}
public boolean mouseDown( Event userAction, int x, int y ) {
displayMessage("click!... " + x + " " + y);
return true;
}
public boolean keyDown( Event userAction, int key ) {
displayMessage( "Key pressed!... " + key );
return true;
}
public void displayMessage( String message ) {
System.out.println( message );
eventMessage = message;
repaint(); // redraw the window
}
public void paint( Graphics display ) {
display.drawString( eventMessage , 30, 40 );
}
public static void main( String args[] ){
EventMethods mainWindow;
mainWindow = new EventMethods( 300, 200 );
}
}
Output

Return, handleEvent, Convenience methods
If you completely handle an event then return true
In handleEvent if you do not handle or completely handle an event then return
super.handleEvent( userAction );
public boolean handleEvent( Event userAction )
{
if ( userAction.id == Event.MOUSE_DOWN )
{
displayMessage( "MOUSE_DOWN" );
return true;
}
else if ( userAction.id == Event.MOUSE_ENTER )
displayMessage( "MOUSE_ENTER" );
return super.handleEvent( userAction );
}
In convenience method if you do not handle or completely handle an event then
return false
Do NOT return super.handleEvent in convenience method
public boolean mouseDown( Event userAction, int x, int y ) {
displayMessage("Mouse down" + x + " " + y);
return true;
}
public boolean mouseEnter( Event userAction, int x, int y ) {
displayMessage("Mouse Enter" + x + " " + y);
return false;
}
How do handleEvent and Event Methods Work?
import java.awt.*;
class EventMethods extends Frame {
public EventMethods( int WidthInPixels, int heightInPixels ) {
setTitle( "Event Methods" );
resize( WidthInPixels, heightInPixels );
show();
}
public boolean handleEvent( Event userAction ){
if ( userAction.id == Event.MOUSE_DOWN )
displayMessage( "Mouse down in handle Event" );
return super.handleEvent( userAction );
}
public boolean mouseDown( Event userAction, int x, int y ) {
displayMessage( "Mouse down in mouse down");
return false;
}
public void displayMessage( String message ) {
System.out.println( message );
}
public void paint( Graphics display ) {
display.drawString( "Constant" , 30, 40 );
}
public static void main( String args[] ){
EventMethods mainWindow;
mainWindow = new EventMethods( 300, 200 );
}
}
Output
Mouse down in handle Event
Mouse down in mouse down
How do handleEvent and Event Methods Work?
First handleEvent is sent to the window
If your class has handleEvent it is run
If not the default handleEvent is run
super.handleEvent is the default handleEvent
The default handleEvent will call mouseDown, etc.
If your class has mouseDown it is then run
If your class does not have mouseDown the default mouseDown is run
The default mouseDown does nothing
The default methods are in java.awt.Component
The paint method has a graphics object as an argument
public void paint( Graphics display ) {
display.drawString( "Constant" , 30, 40 );
}
The graphics class contains methods for drawing
Graphics Methods
| clearRect(int, int, int, int) | drawString(String, int, int) |
| clipRect(int, int, int, int) | fill3DRect(int, int, int, int, boolean) |
| copyArea(int, int, int, int, int, int) | fillArc(int, int, int, int, int, int) |
| create() | fillOval(int, int, int, int) |
| create(int, int, int, int) | fillPolygon(int[], int[], int) |
| dispose() | fillPolygon(Polygon) |
| draw3DRect(int, int, int, int, boolean) | fillRect(int, int, int, int) |
| drawArc(int, int, int, int, int, int) | fillRoundRect(int, int, int, int, int, int) |
| drawBytes(byte[], int, int, int, int) | finalize() |
| drawChars(char[], int, int, int, int) | getClipRect() |
| drawImage(Image, int, int, Color, ImageObserver) | getColor() |
| drawImage(Image, int, int, ImageObserver) | getFont() |
| drawImage(Image, int, int, int, int, Color, ImageObserver) | getFontMetrics() |
| drawImage(Image, int, int, int, int, ImageObserver) | getFontMetrics(Font) |
| drawLine(int, int, int, int) | setColor(Color) |
| drawOval(int, int, int, int) | setFont(Font) |
| drawPolygon(int[], int[], int) | setPaintMode() |
| drawPolygon(Polygon) | setXORMode(Color) |
| drawRect(int, int, int, int) | toString() |
| drawRoundRect(int, int, int, int, int, int) | translate(int, int) |
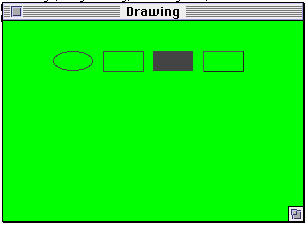
import java.awt.*;
class Drawing extends Frame {
public Drawing ( int WidthInPixels, int heightInPixels ) {
setTitle( "Drawing" );
resize( WidthInPixels, heightInPixels );
setBackground( Color.green);
show();
}
public void paint( Graphics display ) {
display.setColor( Color.darkGray );
int x = 50; int y = 30;
int width = 40; int height = 20;
display.drawOval( x, y, width, height );
x = 100;
display.drawRect( x, y, width, height );
x = 150;
display.fillRect( x, y, width, height );
x = 200;
boolean raised = true;
display.draw3DRect( x, y, width, height, raised );
}
public static void main( String args[] ){
Drawing mainWindow;
mainWindow = new Drawing( 300, 200 );
}
}
Output
Color
Predefined Colors in Color Class
| black | green | pink |
| blue | lightGray | red |
| cyan | magenta | white |
| darkGray | orange | yellow |
| gray | | |
Constructors
Color(float, float, float)
- Creates a color with the specified red, green, and blue values in the range
(0.0 - 1.0).
Color(int)
- Creates a color with the specified combined RGB value consisting of the red
component in bits 16-23, the green component in bits 8-15, and the blue
component in bits 0-7.
Color(int, int, int)
- Creates a color with the specified red, green, and blue values in the range
(0 - 255).
Methods
| brighter() | getHSBColor(float,float,float) |
| darker() | getRed() |
| equals(Object) | getRGB() |
| getBlue() | hashCode() |
| getColor(String) | HSBtoRGB(float,float,float) |
| getColor(String,Color) | RGBtoHSB(int,int,int,float[]) |
| getColor(String,int) | toString() |
| getGreen() | |
Drawing Modes
Normal paint mode is to cover bits as you draw
- In normal draw mode a red line on a red area you will not see the
line
In XOR mode colors are toggled
- There is a current drawing color and an XOR color
- If you draw over an area that is already in the current drawing color, the
XOR color is used
-
-
Change to XOR mode with Graphics method
- setXORMode( Color XORColor )
Change to paint mode with Graphics method
- setPaintMode()
import java.awt.*;
class FancyHello extends Frame {
public FancyHello()
{
int pointSize = 24;
setFont( new Font( "TimesRoman", Font.BOLD, pointSize ));
setBackground( Color.black );
setTitle( "Hi Mom" );
resize( 150, 150);
show();
}
public void paint( Graphics display )
{
int x = 50;
int y = 60;
display.setColor( Color.white );
display.drawString( "Hello", x, y );
display.setFont( new Font("Courier", Font.ITALIC, 12 ));
x = 50;
y = 100;
display.drawString( "World", x, y );
}
public static void main( String args[] )
{
new FancyHello();
}
}
Output

Font Issues
What Fonts are Available?
import java.awt.Toolkit;
class WhatFonts {
public static void main( String args[] )
{
Toolkit platformInfo = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
String[] availbleFonts = platformInfo.getFontList();
for ( int index = 0; index < availbleFonts.length; index++ )
System.out.println( availbleFonts[ index ] );
}
}
Standard? Answer
Dialog
Helvetica
TimesRoman
Courier
Symbol
What Font Styles are Available?
Font.PLAIN
Font.BOLD
Font.ITALIC
These can be mixed
new Font("Courier", Font.ITALIC + Font.BOLD, 12 )
Font Issues
How many pixels in a string?
Use FontMetrics to find the answer
import java.awt.*;
class TextSize extends Frame
{
public TextSize()
{
setTitle( "Text Size" );
resize( 300, 200);
show();
}
public void paint( Graphics display )
{
Font largeText = new Font( "TimesRoman", Font.BOLD, 24 );
FontMetrics largeTextSize;
largeTextSize = display.getFontMetrics( largeText );
display.setFont( largeText );
display.setColor( Color.black );
int x = 50;
int y = 90;
display.drawString( "Hello ", x, y );
x = x + largeTextSize.stringWidth( "Hello " );
display.drawString( "World", x, y );
}
public static void main( String args[] )
{
new TextSize();
}
}
Output

Types of Cursors
| CROSSHAIR_CURSOR | NW_RESIZE_CURSOR |
| DEFAULT_CURSOR | S_RESIZE_CURSOR |
| E_RESIZE_CURSOR | SE_RESIZE_CURSOR |
| HAND_CURSOR | SW_RESIZE_CURSOR |
| MOVE_CURSOR | TEXT_CURSOR |
| N_RESIZE_CURSOR | W_RESIZE_CURSOR |
| NE_RESIZE_CURSOR | WAIT_CURSOR |
These are defined in java.awt.Frame
The setCursor method in Frame changes the mouse Cursor
Cursor Example
class Cursors extends Frame {
public Cursors( int WidthInPixels, int heightInPixels ) {
setTitle( "Cursors" );
resize( WidthInPixels, heightInPixels );
show();
}
public boolean mouseDown( Event userAction, int x, int y ) {
setCursor( Frame.HAND_CURSOR );
return true;
}
public boolean mouseUp( Event userAction, int x, int y ) {
try {
long millisecondDelay = 500;
setCursor( Frame.WAIT_CURSOR );
Thread.sleep( millisecondDelay );
setCursor( Frame.TEXT_CURSOR );
Thread.sleep( millisecondDelay );
setCursor( Frame.MOVE_CURSOR );
Thread.sleep( millisecondDelay );
setCursor( Frame.DEFAULT_CURSOR );
}
catch ( InterruptedException interrupt ) { }
return true;
}
public void paint( Graphics display ) {
display.drawString( "Cursors" , 30, 40 );
}
public static void main( String args[] ){
Cursors mainWindow = new Cursors( 300, 200 );
mainWindow.setCursor( Frame.WAIT_CURSOR );
}
}
Frame
Public Variables
| CROSSHAIR_CURSOR | NW_RESIZE_CURSOR |
| DEFAULT_CURSOR | S_RESIZE_CURSOR |
| E_RESIZE_CURSOR | SE_RESIZE_CURSOR |
| HAND_CURSOR | SW_RESIZE_CURSOR |
| MOVE_CURSOR | TEXT_CURSOR |
| N_RESIZE_CURSOR | W_RESIZE_CURSOR |
| NE_RESIZE_CURSOR | WAIT_CURSOR |
Frame Methods
| addNotify() | paramString() |
| dispose() | remove(MenuComponent) |
| getCursorType() | setCursor(int) |
| getIconImage() | setIconImage(Image) |
| getMenuBar() | setMenuBar(MenuBar) |
| getTitle() | setResizable(boolean) |
| isResizable() | setTitle(String) |
 CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design









