 CS660 Combinatorial Algorithms
CS660 Combinatorial Algorithms
Fall Semester, 1996
Past CS 660 Exams
[To Course Index]
San Diego State University -- This page last updated Oct 25, 1996

Contents of Past CS 660 Exams
- Midterm Fall 1995
- Final Fall 1995
- Midterm Fall 1994
- Final Fall 1994
Solve any six of the following problems. Indicate which six problems you want
graded.
1. Discuss the strong points of (a, b)-trees, splay trees, and AVL
trees. That is which conditions favor each algorithm?
2. Expected cost of an algorithm (as was done for skiplists and
randomized search trees) and amortized analysis both provide information about
the performance of an algorithm over a sequence of operations. What is the
difference in what each type of analysis tells us about an algorithm?
3. Prove or disprove the following:
- a. f(n) = o(g(n))) implies that g(n) = [[omega]](f(n))
-
- b. f(n) = o(g(n)) implies that f(n) > g(n) for all n
4. a. Solve the recurrence relation T(n) = T(n/4) + c where T(1) = T(2)
= T(3) = 1. You may assume that n is a power of 4
- b. Explain how this recurrence relation is related to (a, b)
trees.
5. Does performing a top-down splay to node "a" in tree T always produce
the same resultant tree as performing a bottom-up splay from node "a" in tree
T? Explain your answer.
6. We have three operations on a stack: pop, push, and copy. The actual
cost of each operation is: pop= +1, push = +1, copy = current size of the
stack. Every K operations we copy the stack. The stack is not bounded in size.
That is the stack can become as large as desired. What do the amortized costs
of pop and push need to be to make the amortized cost of copy to be zero.
7. What is the amortized number of rotations done in deleting a node
from the following trees:
- AVL, Red-Black, Splay, Randomized Search tree
8. a. What is a Treap?
- b. Describe how to insert a node in a Treap.
9. Show that the height of a B-tree of degree t with n nodes is at most
C*logtn + K.
10. Show that a Red-Black tree is a B-tree of degree 2.
11. What advantage(s) does the transpose algorithm have over
move-to-front algorithm?
12. Discuss the difference in cost between using a dynamic table instead
of a linked list.
Solve any six of the following problems. Indicate which six problems you want
graded.
1. a) What is the time complexity of the Ford-Fulkerson algorithm?
b) What is the time complexity of the Edmond-Karp algorithm?
c) Give an example of a network flow where the Ford-Fulkerson algorithm is
faster than the Edmond-Karp algorithm.
2. Show the order of the flows found by the Edmond-Karp algorithm on the
following graph.
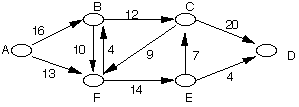
3. Prove or disprove the following:
- a. f(n) + g(n) =
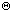 (min(
f(n), g(n) ).
(min(
f(n), g(n) ).
- b. f(n) = O( g(n) ) and f(n) =
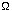 ( g(n) ) implies f(n) =
( g(n) ) implies f(n) =
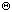 (
g(n) ).
(
g(n) ).
4. Prove the follow part of the max-flow min-cut theorem. Let f be a
flow on a flow network G = (V, E) with source s and sink t. If |f| = c(S, T)
for some cut (S, T) of G then show that f is a maximum flow in G. (Note s
 S and t
S and t
 T.)
T.)
5. The longest simple cycle problem is: Given a graph G = (V, E), does G
contain a simple cycle of length greater than B. Show that the longest simple
cycle problem is NP-complete.
6. a) State Cooks theorem.
b) Define the following terms: P, NP, polynomial transformation.
7. Characterize the types of problems that one can solve using dynamic
programming.
8. Under what conditions will a dynamic programming algorithm perform in
O(n2) time?
9. a) Given a potential function describe how to determine the
amortized cost for the operations of the algorithm.
b) Describe the accounting method of amortized analysis.
10. Explain how to insert a key into a skiplist and maintain the list as
a skiplist.
11. Discuss the strong points of splay trees, red-black trees, and
B-trees. That is which conditions favor each algorithm?
12. Let S and T be binary search structures. Assume that all elements in
S are less than all elements in T. We need to implement a join operation.
Join(S, T) returns a single binary search structure that contains all elements
of S and T. Note S and T can be modified by the join operation. Which of the
structures: red-black trees, splay trees, skiplists, AVL trees, (a, b)-trees
would permit an efficient implementation of join? Explain your answer.
Solve any six of the following problems.
1. We are keeping an ordered list of items in an array. Provide a
potential function which gives an amortized cost of O(n) to insert an item, an
O(1) to delete an item.
2. A tree T is a (2,8)-tree if
- i)
- All leaves of T have the same depth
- ii)
- All internal nodes v of T have at most 8 children (ie each node can have 7
keys)
- iii)
- All internal nodes have at least 2 children
- iiii)
- All keys are stored in order, that is the tree is a search tree.
a) Show how to convert a (2,8)-tree to a binary search tree with the nodes
colored with two colors.
b) What properties hold true in the binary search tree created in a)
3. The greedy algorithm can be used to create the optimal static
ordering for a linear list. Can the greedy algorithm can be used to create the
optimal binary search tree. Explain your answer.
4. a) Use the Hu-Tucker algorithm to construct the optimal alphabetic
tree given the following items and frequency of access.
Item a b c d e
Frequency 1 2 2 3 4
b) What is the time complexity of the Hu-Tucker algorithm?
5. Discuss the time complexity of dynamic programming algorithms.
6. Using just the mathematical analysis and understanding of the
algorithms, discuss the strong points of red-black trees, splay trees, and
skiplists. That is which conditions favor each algorithm?
7. Dynamic programming can be used to solve the following problem:
determine how many ways there are to give x cents in change using pennies,
nickels, and dimes. What is the recursion that will define the optimal
solution. (Hint: how would you solve it with just pennies and nickels? with
just pennies?)
8. Add 27 to the following splay tree using top-down splay. Show your
work.
-
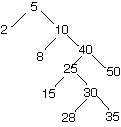
10. Average case analysis and amortized analysis both provide
information about the performance of an algorithm over a sequence of
operations. What is the difference?
11. Under what conditions will move-to-front perform better than optimal
static ordering of a linear list?
1. Prove or disprove the following:
a. f(n) = O(g(n))) implies that g(n) = O(f(n))
b. f(n) = O(g(n)) implies that f(n) =< g(n) for all n
2. Contrast the performance of transpose and move-to-front
self-organizing linear lists.
3. a. What is the potential function on a splay tree?
b. Explain how to implement the following using the splay operation
join (a, b):
- Return tree formed by combining tree "a", and tree "b". Assumes that every
item in "a" has key less then every item in "b"
split (i, t):
- Split tree t, containing item i, into two trees: "a", containing all items
with key less or equal to "i"; and "b", containing all items with key greater
than "i"
delete(i, t):
- delete i from tree t
4. Describe the process of inserting an item into a skiplist. How does
changing the value of p effect on the performance of the skiplist?
5. A red-red-black tree is a binary search tree that satisfies the
following conditions:
- 1. Every node is either red or black
- 2. Every leaf (nil) is black
- 3. If a node is red and it's parent is red, then both its children are black
- 4. Every simple path from a node to a descendant leaf contains the same
number of black nodes (the black-height of the tree)
What is the largest number of internal nodes in a red-red-black tree with
black-height k?
6. Let f be a flow in a flow network G = (V, E) with source s and sink t
argue that if the residual network Gf contains no augmenting paths
then |f| = c(S,T) for some cut (S, T) of G.
7. Let f be a flow in a flow network G = (V, E) with source s and sink
t. Let cf(u,v) be the residual capacity of the edge uv in E. Show
that cf(u, v) + cf(v, u) = c(u, v) + c(v, u).
8.
T or F The probability of a search on a skiplist of size 256 being three times
the expected value is less than the probability of a division error on Intel's
pentium chip.
T or F If P != NP then no problem in NP can be solved in polynomial time.
9. A binary heap is a complete binary search tree with the following
property: the value stored in a node, X, is smaller than the values stored in
the children of X. Instructions Insert and extract-min can be performed on a
heap with n items in O(lg(n)) worst case. (The operations have to maintain the
heap property.) Give a potential function such that the amortized cost of
Insert is O(lg(n)) and the amortized cost of Extract-min is O(1).
10.
a. Prove that if language
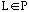 then
then
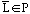 .
(
.
(
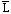 is the complement of L).
is the complement of L).
b. Discuss the statement: if
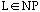 then
then
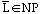 .
.
 CS660 Combinatorial Algorithms
CS660 Combinatorial Algorithms CS660 Combinatorial Algorithms
CS660 Combinatorial Algorithms
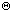 (min(
f(n), g(n) ).
(min(
f(n), g(n) ).
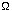 ( g(n) ) implies f(n) =
( g(n) ) implies f(n) =
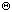 (
g(n) ).
(
g(n) ). S and t
S and t
 T.)
T.)
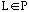 then
then
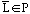 .
(
.
(
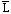 is the complement of L).
is the complement of L).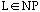 then
then
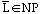 .
.