
Fall Semester, 1998
Arrays, Strings, Control Structures
© 1998, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney
San Diego State University -- This page last updated 19-Sep-98

|
CS 596 Java Programming Fall Semester, 1998 Arrays, Strings, Control Structures |
|
|---|---|---|
|
© 1998, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney San Diego State University -- This page last updated 19-Sep-98 |
public class SimpleReferenceExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
// Reference allocated, no array space allocated
float[] sampleArray;
//allocate array locations on heap
sampleArray = new float[ 12 ];
// Indexing starts at 0 like C/C++
sampleArray[ 0 ] = 3.2F;
int[] integerArray = new int[ 3 ];
// Reference refers to new array.
// Old array available for garbage collection
sampleArray = new float[ 2 ];
}
}
public class ArrayExamples
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
// Two locations to place [ ]
int integerArray[ ];
int[ ] alias;
integerArray = new int[ 10 ]; // Indexed from 0 to 9
// Note use of .length to get array size
for ( int index = 0; index < integerArray.length; index++ )
integerArray[ index ] = 5;
alias = integerArray; // Arrays are references
alias[ 3 ] = 10;
System.out.println( integerArray[ 3 ] ); //Prints 10
integerArray = new int[ 8 ];
System.out.println( integerArray[ 3 ] ); //Prints 0, Why?
System.out.println( alias[ 3 ] ); //Prints 10
System.out.println( integerArray ); //Prints [I@5e300868
}
}
public classArrayExamples
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int[] integerArray = new int[ 4 ];
integerArray[ 1 ] = 12
integerArray = new int[ 2 ]; // Memory Leak - No!
integerArray[ 1 ] = 5;
int[] aliasForArray = integerArray;
aliasForArray[ 1 ] = 10;
System.out.println( integerArray[ 1 ] ); //Prints 10
}
}
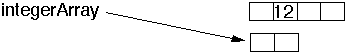
int[] integerArray = new int[ 4 ];

integerArray[ 1 ] = 12
integerArray = new int[ 2 ]; // Memory Leak - No!
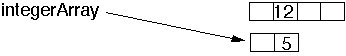
integerArray[ 1 ] = 5;
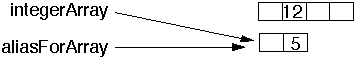
int[] aliasForArray = integerArray;
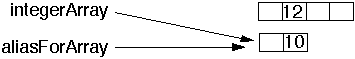
aliasForArray[ 1 ] = 10;


public class BoundsAndInitialValueExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int[ ] data = new int[ 2];
System.out.println( "Data[1]= " + data[1] );
data[ 12] = 2;
System.out.println( "After assignment" );
}
}
Data[1]= 0 java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException at BoundsAndInitialValueExample.main(BoundsAndInitialValueExample.java:9)
public class InitializingArrays
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
// Short Declaration syntax
int[ ] odds = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9 };
char[ ] vowels = { 'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u' };
String[] names;
// Assignment syntax - new in JDK 1.1.x
names = new String[] { "Sam", "Sally", "Pete" };
// Can use longer syntax in declarations
char[] abc = new char[] { 'a', 'b', 'c' };
//You can not use short syntax in assignments
double[ ] trouble;
trouble = { 1.2, 2.3, 5.4 }; //Compiler Error
}
}
public class MultidimensionalArrayExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int[][] squareArray = new int [ 10 ] [ 20 ];
squareArray[ 2 ] [ 5 ] = 25;
int[][][] threeDArray = new int [ 10 ] [ 20 ][ 5 ];
int[][] triangularArray;
triangularArray = new int [ 30 ] [ ] ;
// Allocate rows of different length!
for ( int row = 0; row < triangularArray.length; row ++ )
triangularArray [ row ] = new int [ row ];
// Fill array locations
for ( int row = 0; row < triangularArray.length; row ++ )
for ( int col = 0; col < triangularArray[ row ].length; col++ )
triangularArray[ row ][ col ] = 10;
// Initializers for multidimensional arrays,
// note the different size rows
int[ ] [ ] oddShape = {
{ 1 , 2, 3 } ,
{ 1, 2 },
{ 4, 5, 6, 7 }
};
}
}
|
binary
search
|
equals
|
|
fill
|
sorting
|
import java.util.Arrays;
public class NewArrayOperations
{
public static void main( String[ ] args )
{
int [] list = { 9, 2, 5, 7, 1 };
// Sorts using fancy quicksort
Arrays.sort( list );
// if not found, then return -1
int foundIndex = Arrays.binarySearch( list, 7 );
System.out.println( "Found 7 at: " + foundIndex );
int[ ] ones = new int[ 12 ];
// Fill array with value 1
Arrays.fill( ones, 1 );
System.out.println( "One: " + ones[10] );
}
}
Found 7 at: 3 One: 1
public class StringExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
String firstName = " Roger ";
String lastName = " Whitney ";
String fullName = firstName + lastName;
System.out.println( fullName );
firstName = firstName.toLowerCase();
lastName = lastName.toUpperCase();
System.out.println( firstName );
firstName = firstName.trim(); // trim leading, trailing
lastName = lastName.trim(); // white space
lastName = lastName.replace( 'I', 'a' );
System.out.println( firstName + lastName );
String floatAsString = String.valueOf( 13.4e+5f);
System.out.println( floatAsString );
}
}
Roger Whitney
roger
rogerWHaTNEY
1.34e+06
firstName = firstName.toLowerCase();
| charAt(int) | replace(char,char) |
| compareTo(String) | startsWith(String) |
| concat(String) | substring(int,int) |
| copyValueOf(char[]) | toCharArray() |
| endsWith(String) | toLowerCase() |
| equals(Object) | toUpperCase() |
| equalsIgnoreCase(String) | trim() |
| getChars(int,int,char[],int) | valueOf(int) |
| indexOf(String) | valueOf(long) |
| lastIndexOf(String) | valueOf(float) |
| length() | valueOf(double) |
| regionMatches(int,String,int,int) |
public class StringTest
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
String me = "Roger";
if ( me == "Roger" )
System.out.println( "Yes, I am me" );
else
System.out.println( "No, I am not me?" );
String shortName = me.substring( 0, 3 );
System.out.println( shortName );
if ( shortName == "Rog" )
System.out.println( "Very Good" );
else
System.out.println( "Trouble here" ); //How is this possible?
if ( shortName.equals( "Rog" ) )
System.out.println( "Do it this way" );
}
}
if ( me == "Roger" )
System.out.println( "Yes, I am me" );
else
System.out.println( "No, I am not me?" );
if ( shortName == "Rog" )
public class CommandLineExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
System.out.println( "Args length: " + args.length );
for ( int k = 0; k < args.length; k++ )
{
System.out.println( "Argument " + k + "\t" + args[ k ] );
};
Float secondArgument = Float.valueOf( args[ 1 ] );
System.out.println( secondArgument );
}
}
rohan 16-> java CommandLineExample 1 2 3 4 5 Args length: 5 Argument 0 1 Argument 1 2 Argument 2 3 Argument 3 4 Argument 4 5 2
public class Control
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int a = 5;
int b = 10;
if ( a > b ) System.out.println( "a is bigger ");
if ( a > b )
System.out.println( "a is bigger ");
else
System.out.println( "b is bigger ");
switch ( a )
{ //Controlling expression converted to int
case 4:
b++;
break;
case 10:
b--;
break;
default: // optional
System.out.println( "Default action" );
};
while ( a < b )
{
a++;
};
for ( int loop = 0; loop < a; loop++ )
{
System.out.println( a );
};
System.out.println( loop ); // Error, loop does not
// exist here
do
{
System.out.println( a-- );
System.out.println( b );
}
while ( a > b );
int max = ( a > b ) ? a : b;
if ( ( a > 5 ) && ( b < 10 ) )
System.out.println( "Good" );
a += ( a = 5 );
}
}
public class BreakExample {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
for ( int row = 0; row < 5; row++ ) {
for ( int column = 0; column < 4 ; column++ ) {
System.out.println( row + "\t" + column );
if ( ((row + column) % 2 ) == 0 )
break;
System.out.println( " After if " );
}
};
Outer:
for ( int row = 0; row < 5; row++ ) {
for ( int column = 0; column < 4; column++ ) {
System.out.println( row + "\t" + column );
if ( ((row + column) % 2 ) == 0 )
break Outer;
System.out.println( " After if " );
}
}
}
}
| 0 0 | 3 0 |
| 1 0 | After if |
| After if | 3 1 |
| 1 1 | 4 0 |
| 2 0 | 0 0 |
public class SampleFunction {
public static int subtractOne( int decreaseMe ) {
return decreaseMe - 1;
}
public static void main( String[] args ) {
int startValue = 5;
int smaller = subtractOne( startValue );
int larger = addOne( startValue );
System.out.println( "smaller = " + smaller + "\n" +
"larger = " + larger );
}
public static int addOne( int increaseMe ) {
return increaseMe + 1;
}
}
smaller = 4 larger = 6
public class TestParameter
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
int startValue = 5;
noChange( startValue );
System.out.println( startValue );
}
public static void noChange( int fixed )
{
fixed = fixed + 10;
}
}
5
public class ReturnExample
{
public static int change( int input )
{
return input + 10;
}
public static void voidReturnExample( int data )
{
if (data > 10 )
return;
if (data < 5)
System.out.println( "Under 5");
else
System.out.println( "Over 5");
}
}
public class ArrayAsParameter
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int[] integerArray = new int[ 10 ];
integerArray[ 1 ] = 5;
modifyElements( integerArray, 10 );
System.out.println( integerArray[ 1 ] );
}
public static void modifyElements( int[] changeMe, int newValue )
{
for ( int index = 0; index < changeMe.length; index++ )
changeMe[ index ] = newValue;
}
}
10
public class ArrayAsParameter
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int[] integerArray = new int[ 10 ];
integerArray[ 1 ] = 5;
doesNotWork( integerArray );
System.out.println( integerArray[ 1 ] );
}
public static void doesNotWork( int[] changeMe )
{
changeMe = new int[ 10 ];
for ( int index = 0; index < changeMe.length; index++ )
changeMe[ index ] = 555;
}
}
public class FinalExamples
{
public static void fixed( final double fixedValue )
{
double newValue = fixedValue + 1;
fixedValue = fixedValue + 1; //Compile error
final int aConstant = (int) fixedValue;
final int aBlankFinal; //This is ok
aBlankFinal = 12; //This is ok
aBlankFinal = 13; //Compile error
}
public static void fixedArray( final int[] data )
{
data[2] = 4; // This is ok, Why?
data[2] = 5; // This is ok
data = new int[ 4]; //Compile error
}
}