
Spring Semester, 2001
Factory Method & Prototype
© 2001, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney
San Diego State University -- This page last updated 07-Mar-01

|
CS 635 Advanced Object-Oriented Design & Programming Spring Semester, 2001 Factory Method & Prototype |
|
|---|---|---|
|
© 2001, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney San Diego State University -- This page last updated 07-Mar-01 |
Factory Method
A template method for creating objects
Example - Maze Game
Classes for Mazes
Now a maze game has to make a maze
Maze Class Version 1 class MazeGame { public Maze createMaze() { Maze aMaze = new Maze(); Room r1 = new Room( 1 ); Room r2 = new Room( 2 ); Door theDoor = new Door( r1, r2); aMaze.addRoom( r1 ); aMaze.addRoom( r2 ); etc. return aMaze; } }
How do we make other Mazes?
Subclass MazeGame, override createMaze
class BombedMazeGame extends MazeGame { public Maze createMaze() { Maze aMaze = new Maze(); Room r1 = new RoomWithABomb( 1 ); Room r2 = new RoomWithABomb( 2 ); Door theDoor = new Door( r1, r2); aMaze.addRoom( r1 ); aMaze.addRoom( r2 ); etc.
Note the amount of cut and paste!
How do we make other Mazes?
Use Factory Method
class MazeGame { public Maze makeMaze() { return new Maze(); } public Room makeRoom(int n ) { return new Room( n ); } public Wall makeWall() { return new Wall(); } public Door makeDoor() { return new Door(); } public Maze CreateMaze() { Maze aMaze = makeMaze(); Room r1 = makeRoom( 1 ); Room r2 = makeRoom( 2 ); Door theDoor = makeDoor( r1, r2); aMaze.addRoom( r1 ); aMaze.addRoom( r2 ); etc return aMaze; } }
Now subclass MazeGame override make methods
CreateMaze method stays the same
class BombedMazeGame extends MazeGame { public Room makeRoom(int n ) { return new RoomWithABomb( n ); } public Wall makeWall() { return new BombedWall(); }
Applicability
Use when
Consequences
Implementation
Two Major Varieties
abstract class MazeGame
{
public Maze makeMaze();
public Room makeRoom(int n );
public Wall makeWall();
public Door makeDoor();
etc.
}
class MazeGame
{
public:
virtual Maze* makeMaze() = 0;
virtual Room* makeRoom(int n ) = 0;
virtual Wall* makeWall() = 0;
virtual Door* makeDoor() = 0;
Implementation - Continued Parameterized Factory Methods
Let the factory method return multiple products
class Hershey { public Candy makeChocolateStuff( CandyType id ) { if ( id == MarsBars ) return new MarsBars(); if ( id == M&Ms ) return new M&Ms(); if ( id == SpecialRich ) return new SpecialRich(); return new PureChocolate(); }
class GenericBrand extends Hershey { public Candy makeChocolateStuff( CandyType id ) { if ( id == M&Ms ) return new Flupps(); if ( id == Milk ) return new MilkChocolate(); return super.makeChocolateStuff(); } }
C++ Templates to Avoid Subclassing
template <class ChocolateType> class Hershey { public: virtual Candy* makeChocolateStuff( ); } template <class ChocolateType> Candy* Hershey<ChocolateType>::makeChocolateStuff( ) { return new ChocolateType; } Hershey<SpecialRich> theBest;
Java forName and Factory methods
With Java's reflection you can use a Class or a String to specify which type of object to create
Using a string replaces compile checks with runtime errors
class Hershey { private String chocolateType; public Hershey( String chocolate ) { chocolateType = chocolate; } public Candy makeChocolateStuff( ) { Class candyClass = Class.forName( chocolateType ); return (Candy) candyClass.newInstance(); } Hershey theBest = new Heshsey( "SpecialRich" );
Clients Can Use Factory Methods
class CandyStore { Hershey supplier; public restock() { blah if ( chocolateStock.amount() < 10 ) { chocolateStock.add( supplier.makeChocolateStuff() ); } blah
Prototype
Intent
Specify the kinds of objects to create using a prototypical instance, and create new objects by copying this prototype
Applicability
Use the Prototype pattern when
Implementation/Sample Code
Simple Example
class Prototype { public Prototype clone() { code to make a copy of current Prototype object return clone; } // add what ever else you want the class to do } class Protoplasm extends Prototype { public Prototype clone() { code to make a copy of current Protoplasm object return clone; } // add more other stuff } ClientCodeMethod( Prototype example ) { Prototype myCopy = example.clone(); // do some work using myCopy }
Cloning Issues
How to in C++ - Copy Constructors class Door { public: Door(); Door( const Door&); virtual Door* clone() const; virtual void Initialize( Room*, Room* ); // stuff not shown private: Room* room1; Room* room2; } Door::Door ( const Door& other ) //Copy constructor { room1 = other.room1; room2 = other.room2; } Door* Door::clone() const { return new Door( *this ); }
How to in Java - Object clone()
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException
class Door implements Cloneable
{
public void Initialize( Room a, Room b)
{ room1 = a; room2 = b; }
public Object clone() throws
CloneNotSupportedException
{
return super.clone();
}
Room room1;
Room room2;
}
Shallow Copy Verse Deep Copy
Original Objects
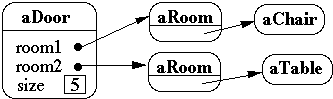
Shallow Copy
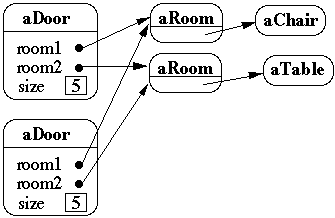
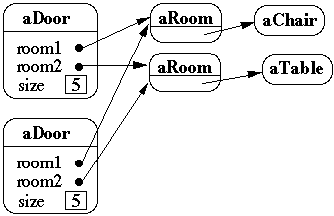
Shallow Copy Verse Deep Copy
Original Objects
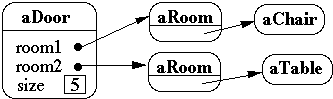
Deep Copy
Template or Boilerplate Objects
May wish to specify how an object differs from a standard configuration
Example: Insurance policy
Consequences