
Spring Semester, 2005
Model-View-Controller
© 2005 All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney
San Diego State University -- This page last updated April 21, 2005

|
Advanced Object-Oriented Design & Programming
Spring Semester, 2005 Model-View-Controller |
|
|---|---|---|
|
© 2005 All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney San Diego State University -- This page last updated April 21, 2005 |
CS 635 Advanced Object-Oriented Design & Programming
Spring Semester, 2005
Doc 16 Model-View-Controller
Contents
Copyright ©, All rights reserved. 2005 SDSU & Roger Whitney, 5500 Campanile Drive, San Diego, CA 92182-7700 USA. OpenContent ( http://www.opencontent.org/opl.shtml ) license defines the copyright on this document.
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 2 |
References
Pattern-Oriented Software Architecture: A System of Patterns v1, Buschman, Meunier, Rohnert, Sommerlad, Stal, 1996, pp 125-143
Domain-Driven Design, Eric Evans, 2004, Addison-Wesley
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 3 |
Interactive application with human-computer interface
Same data may be displayed differently
Display & application must reflect data changes immediately
UI changes should be easy and even possible at runtime
UI changes & additions should not affect core application code
Changing look & feel or port to other platforms should not affect core application code
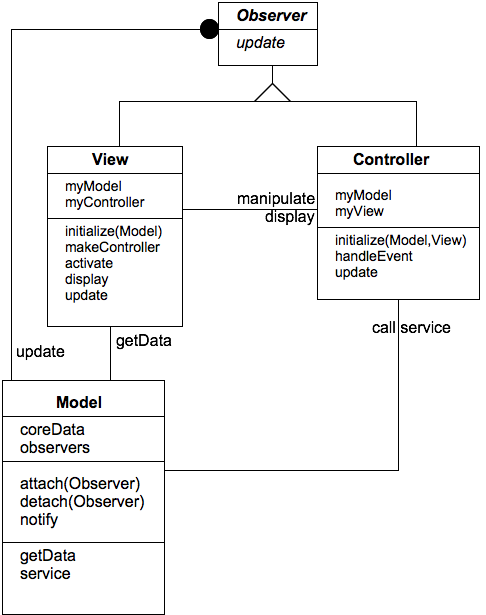
Divide application into three parts:
Model (core application)
View (display, output)
Controller (user input)
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 4 |
Model
Core application code
Contains a list of observers (view & controller)
Has a broadcast mechanism to inform views of a change
Same mechanism as subject in Observer pattern
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 5 |
View
Creates & initializes its controller
Displays information to user
Implements the update procedure
Obtains data from model
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 6 |
Controller
Handles input from user as events
Keystrokes
Mouse clicks
Mouse movements
Maps each event to proper action on model and/or view
Many people misinterpret what a controller does
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 7 |
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 8 |
Controller
Make up the user interface
Most (all?) GUI frameworks combine these
VW Smalltalk contains both, but hides controller from programmer
|
Some Existing Smalltalk Controllers & Views |
|
|
Controllers |
Views |
|
ApplicationDialogController BasicButtonController ClickWidgetController ColoredAreaController ComboBoxButtonController ComboBoxInputBoxController ComboBoxListController ControllerWithMenu ControllerWithSelectMenu DataSetController DataSetControllerProxy DelayingWidgetController DrawingController DropDownListController EmulatedDataSetController EmulatedSequenceController EmulationScrollBarController HierarchicalSequenceController InputBoxController |
ActionButtonView AutoScrollingView BasicButtonView BooleanWidgetView CheckButtonView ClickWidget ComboBoxButtonView ComboBoxInputFieldView ComboBoxListView ComposedTextView DataSetView DefaultLookCheckButtonView DefaultLookRadioButtonView EmulationScrollBar GeneralSelectionTableView HierarchicalSequenceView HorizontalTabBarView HorizontalTopTabBarView InputFieldView |
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 9 |
public class Counter
{
private int count = 0;
public void increase() { count++;}
public void decrease() { count--;}
public String toString() { return String.valueOf(count);}
}
Create a view like:
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 10 |
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import java.awt.Panel;
import java.awt.TextField;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class Counter extends Frame implements ActionListener
{
private static final int NUMBER_OF_COLUMNS = 10;
private TextField value = new TextField(NUMBER_OF_COLUMNS);
private Button increase = new Button("Increase");
private Button decrease = new Button("Decrease");
private int count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new Counter(200, 100);
}
public Counter(int widthInPixels, int heightInPixels)
{
configureWindowFrame(widthInPixels, heightInPixels);
add(textPanel());
add(buttonPanel());
initializeGuiWidgets();
show();
}
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 11 |
First Attempt Continued
private void configureWindowFrame(
int widthInPixels, int heightInPixels)
{
setTitle("Counter");
setSize(widthInPixels, heightInPixels);
setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1));
}
private void initializeGuiWidgets()
{
// Make Model observer of GUI widgets?
increase.addActionListener(this);
decrease.addActionListener(this);
value.addActionListener(this);
value.setText(this.toString());
}
private Panel buttonPanel()
{
Panel buttons = new Panel(new FlowLayout());
buttons.add(increase);
buttons.add(decrease);
return buttons;
}
private Panel textPanel()
{
Panel text = new Panel(new FlowLayout());
text.add(value);
value.setText(toString());
return text;
}
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 12 |
First Attempt Continued
public void increase()
{
count++;
}
public void decrease()
{
count--;
}
public String toString()
{
return String.valueOf(count);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
Object source = event.getSource();
if (source == increase)
increase();
else if (source == decrease)
decrease();
value.setText(toString());
}
}
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 13 |
First Attempt Summary
What was model
Now is listener (observer) to GUI widgets
Knows about each GUI widget
Adding more GUI widgets requires changing class
Not an example of MVC
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 14 |
Model
import java.util.Observable;
public class Counter extends Observable
{
private int count = 0;
public void increase()
{
count++;
changed();
}
public void decrease()
{
count--;
changed();
}
public String toString()
{
return String.valueOf(count);
}
private void changed()
{
setChanged();
notifyObservers();
}
}
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 15 |
View
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class CounterView extends Frame implements Observer
{
private static final int NUMBER_OF_COLUMNS = 10;
private TextField value = new TextField(NUMBER_OF_COLUMNS);
private Button increase = new Button("Increase");
private Button decrease = new Button("Decrease");
private Counter model;
public CounterView(
int widthInPixels, int heightInPixels, Counter count)
{
model = count;
model.addObserver(this);
configureWindowFrame(widthInPixels, heightInPixels);
add(textPanel());
add(buttonPanel());
initializeGuiWidgets();
show();
}
public void update(Observable arg0, Object arg1)
{
value.setText(model.toString());
}
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 16 |
View Continued
private void configureWindowFrame(
int widthInPixels, int heightInPixels)
{
setTitle("Counter");
setSize(widthInPixels, heightInPixels);
setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1));
}
private void initializeGuiWidgets()
{
increase.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent event) {
model.increase();
}
});
decrease.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent event) {
model.decrease();
}
});
}
private Panel buttonPanel()
{
Panel buttons = new Panel(new FlowLayout());
buttons.add(increase);
buttons.add(decrease);
return buttons;
}
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 17 |
View Continued
private Panel textPanel()
{
Panel text = new Panel(new FlowLayout());
text.add(value);
value.setText(model.toString());
return text;
}
}
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 18 |
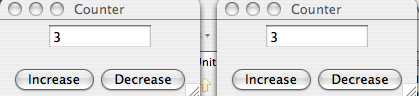
Running an Example
One View
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Counter sampleModel = new Counter();
new CounterView(200, 100, sampleModel);
}
Two Views - Same Model
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Counter sampleModel = new Counter();
new CounterView(200, 100, sampleModel);
new CounterView(200, 100, sampleModel);
}
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 19 |
Another View
A view that shows how many times a counter calls increase
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.TextField;
import java.util.Observable;
import java.util.Observer;
public class IncreaseCountView extends Frame implements Observer
{
private TextField value = new TextField(10);
private int increases = 0;
public IncreaseCountView( Counter count)
{
count.addObserver(this);
setTitle("Counter Increases");
setSize(100, 50);
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
add(value);
value.setText(String.valueOf(increases));
show();
}
public void update(Observable subject, Object changeType)
{
if (changeType.equals("INCREASE"))
{
increases++;
value.setText(String.valueOf(increases));
}
}
}
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 20 |
Changes Needed in the Model
public class Counter extends Observable
{
private int count = 0;
public void increase()
{
count++;
changed("INCREASE"); //Note change
}
public void decrease()
{
count--;
changed("DECREASE"); //Note change
}
public String toString()
{
return String.valueOf(count);
}
private void changed(String type) //Note change
{
setChanged();
notifyObservers(type); //Note change
}
}
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 21 |
Running an Example
Two Views - Same Model
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Counter sampleModel = new Counter();
new CounterView(200, 100, sampleModel);
new IncreaseCountView( sampleModel);
}
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 22 |
Comments
Model had to be changed to:
Notify observers
Indicate type of change
Model is not completely independent of the views
View
Is observer of model
Is observer of GUI widgets
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 23 |
Aspect-Oriented Programming
Allows models to be completely independent of views
More on Aspects
AspectJ - aspects for Java
AspectS - aspects for Smalltalk
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 24 |
“the separation of UI and domain is so often attempted and so seldom accomplished that its negation deserves a discussion”
Eric Evans, Domain-Driven Design
The Pattern
Put all business logic into user interface
Divide the application into different small user interfaces
Use relational databases as back end
Use automated UI building and visual programming tools
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 25 |
Advantages
High and immediate productivity for simple applications
Little training need by the developer
Short development time for small modules
Disadvantages
No reuse – code gets duplicated
Integration of applications difficult
Very difficult to add new functionality to existing application
Difficult to build complex applications
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 26 |
Server pages embeds code into the veiw
Server Pages
Java
<html>
<body>
<%! int x = 1; %>
<%! int y = 2; %>
If we add <%= x %> to <%= y %> we will get <%= x + y %>
</body>
</html>
Smalltalk
<BODY>
<%
x :=1.
y :=2.
%>
<p>
When we add <%= x %> to <%= y %> we get <%= x + y %>
</p>
</BODY>
</HTML>
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 27 |
Servlets
Embed the view in code
Java
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class HelloWorld extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException
{
response.setContentType(" text/html ");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println(" <html> ");
out.println(" <body> ");
out.println(" <head> ");
out.println(" <title>Hello World!</title> ");
out.println(" </head> ");
out.println(" <body> ");
out.println(" <h1>Hello World!</h1> ");
out.println(" </body> ");
out.println(" </html> ");
}
}
| CS635 Spring 2005 | Doc 16, Model-View-Controller Slide # 28 |
Some New Web Frameworks Using MVC
Seaside
Cocoon
Ruby on Rails
Copyright ©, All rights reserved.
2005 SDSU & Roger Whitney, 5500 Campanile Drive, San Diego, CA 92182-7700 USA.
OpenContent license defines the copyright on this document.