
Spring Semester, 2005
Composite & Visitor
© 2005, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney
San Diego State University -- This page last updated 10-Feb-05

|
Advanced Object-Oriented Design & Programming
Spring Semester, 2005 Composite & Visitor |
|
|---|---|---|
|
© 2005, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney San Diego State University -- This page last updated 10-Feb-05 |
CS 635 Advanced Object-Oriented Design & Programming Spring Semester, 2005 Doc 5 Composite & Visitor
Issue: WidgetContainer Operations
Design Patterns: Elements of Resuable Object-Oriented Software, Gamma, Helm, Johnson, Vlissides, Addison-Wesley, 1995, pp. 163-174, 331-344
The Design Patterns Smalltalk Companion, Alpert, Brown, Woolf, Addison-Wesley, 1995, pp. 371-386
Copyright ©, All rights reserved. 2005 SDSU & Roger Whitney, 5500 Campanile Drive, San Diego, CA 92182-7700 USA. OpenContent ( http://www.opencontent.org/opl.shtml) license defines the copyright on this document.
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 2 |
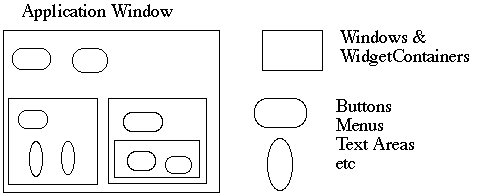
How does the window hold and deal with the different items it has to manage?
Widgets are different that WidgetContainers
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 3 |
class Window
{
Buttons[] myButtons;
Menus[] myMenus;
TextAreas[] myTextAreas;
WidgetContainer[] myContainers;
public void update()
{
if ( myButtons != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myButtons.length(); k++ )
myButtons[k].refresh();
if ( myMenus != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myMenus.length(); k++ )
myMenus[k].display();
if ( myTextAreas != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myButtons.length(); k++ )
myTextAreas[k].refresh();
if ( myContainers != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myContainers.length(); k++ )
myContainers[k].updateElements();
etc.
}
public void fooOperation()
{
if ( blah ) etc.
}
}
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 4 |
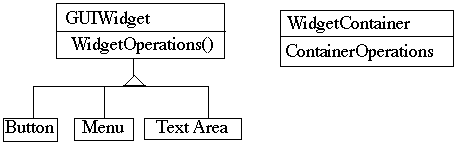
class Window
{
GUIWidgets[] myWidgets;
WidgetContainer[] myContainers;
public void update()
{
if ( myWidgets != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myWidgets.length(); k++ )
myWidgets[k].update();
if ( myContainers != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myContainers.length(); k++ )
myContainers[k].updateElements();
etc.
}
}
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 5 |
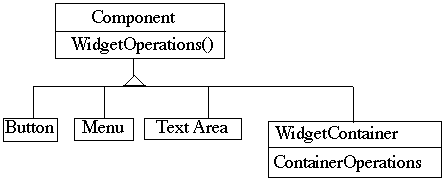
Component implements default behavior for widgets when possible
Button, Menu, etc overrides Component methods when needed
WidgetContainer will have to overrides all widgetOperations
class WidgetContainer
{
Component[] myComponents;
public void update()
{
if ( myComponents != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myComponents.length(); k++ )
myComponents[k].update();
}
}
CS 635 Spring 05 Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 6
WidgetContainer operations tend to relate to adding, deleting and managing widgets
Should the WidgetContainer operations be declared in Component?
Declaring them in the Component gives all subclasses the same interface
All subclasses can be treated alike. (?)
Declaring them in WidgetContainer is safer
Adding or removing widgets to non-WidgetContainers is an error
What should be the proper response to adding a TextArea to a button? Throw an exception?
One out is to check the type of the object before using a WidgetContainer operation
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 7 |
Aid in traversing the structure
class WidgetContainer
{
Component[] myComponents;
public void update()
{
if ( myComponents != null )
for ( int k = 0; k < myComponents.length(); k++ )
myComponents[k].update();
}
public add( Component aComponent )
{
myComponents.append( aComponent );
aComponent.setParent( this );
}
}
class Button extends Component
{
private Component parent;
public void setParent( Component myParent)
{
parent = myParent;
}
etc.
}
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 8 |
Should Component implement a list of Components?
The button etc. will have a useless data member
Child ordering is important in some cases
Who should delete components?
If there is no garbage collection Container is best bet
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 9 |
Use Composite pattern when you want
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 10 |
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 11 |
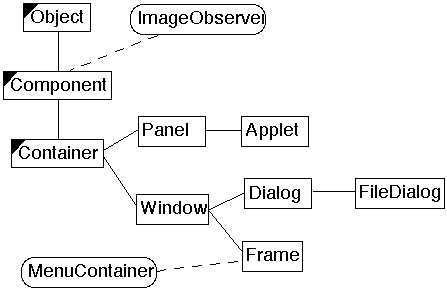
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 12 |
What about preorder visit, postorder visit?
What about an HTML print?
What about printing a 2D representation?
What if this was an expression tree - evaluation?
What if this was a binary search tree - adding, deleting
What about balancing the binary search tree -
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 13 |
Build all the operations into the tree structure
This works in many situations
If you need to add a lot of operations the classes can become cluttered
class BinaryTree {
public String htmlPrint() { blah}
public String 2DPrint() { blah}
public String preorderTraversal() { blah}
public String postorderTraversal() { blah}
public String avlAdd() { blah}
public String RedBlackAdd() { blah}
etc.
}
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 14 |
Use different classes or subclasses for the different types of trees
Does not work in classes we want to be able to mix all combinations
class BinaryTree {
blah
}
class AVLTree extends BinaryTree {
blah
}
class RedBlackTree extends BinaryTree {
blah
}
class PreorderTree extends BinayrTree {
blah
}
etc.
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 15 |
class BinaryTreeNode extends Node {
public void accept(Visitor aVisitor) {
aVisitor.visitBinaryTreeNode( this );
}
etc.
}
class BinaryTreeLeaf extends Node {
public void accept(Visitor aVisitor) {
aVisitor.visitBinaryTreeLeaf( this );
}
etc.
}
abstract class Visitor {
abstract void visitBinaryTreeNode( BinaryTreeNode );
abstract void visitBinaryTreeLeaf( BinaryTreeLeaf );
}
class HTMLPrintVisitor extends Visitor {
public void visitBinaryTreeNode( BinaryTreeNode ) {
HTML print code here
}
etc.
}
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 16 |
Note that a visit to one node requires two method calls
Node example = new BinaryTreeLeaf();
Visitor traveler = new HTMLPrintVisitor();
example.accept( traveler );
example.accept() calls aVisitor.visitBinaryTreeNode(this);
The first method selects the correct method in the Visitor class
The second method selects the correct Visitor class
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 17 |
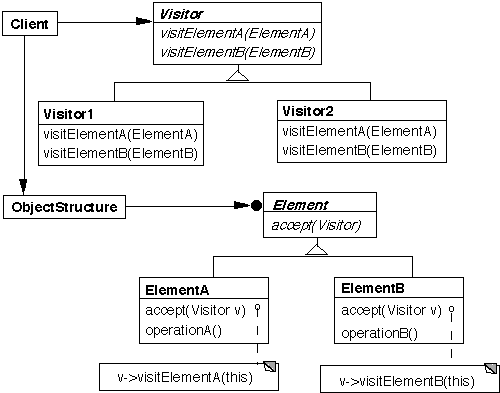
This is more complex than solutions 1 & 2
The structure, an iterator, or the visitor can do the traversal
The visitor is told what type it is acting on, so using the wrong visitor will be a compile error
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 18 |
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 19 |
| CS 635 Spring 05 | Doc 5, Composite & Visitor Slide # 20 |
Visitor pattern requires elements to have an accept method
Sometimes this is not possible
Use reflection to avoid the accept method in the elements
Visitor>>visit: anElement
self
perform: ('visit' , anElement class name , ':') asSymbol
with: anElement
AspectJ provides a way around the use of Element accept methods in aspect oriented Java
AspectS provides a similar process for Smalltalk
Copyright ©, All rights reserved.
2005 SDSU & Roger Whitney, 5500 Campanile Drive, San Diego, CA 92182-7700 USA.
OpenContent license defines the copyright on this document.