 CS 596 Client-Server Programming
CS 596 Client-Server Programming
Classes of Basic Types
[To Lecture Notes Index]
San Diego State University -- This page last updated January 31, 1996

Contents of Classes of Basic Types Lecture
- Classes for Basic Types
- Strings
- String vs. char[] vs. C/C++ char*
- Reading Command Line Arguments
- Numeric Classes
class StringExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
String firstName = " Roger ";
String lastName = " Whitney ";
String fullName = firstName + lastName;
System.out.println( fullName );
firstName = firstName.toLowerCase();
lastName = lastName.toUpperCase();
System.out.println( firstName );
firstName = firstName.trim(); // trim leading, trailing
lastName = lastName.trim(); // white space
lastName = lastName.replace( 'I', 'a' );
System.out.println( firstName + lastName );
String floatAsString = String.valueOf( 13.4e+5f);
System.out.println( floatAsString );
}
}
Output
Roger Whitney
roger
rogerWHaTNEY
1.34e+06
Some String Operations
| charAt(int) | replace(char,char) |
| compareTo(String) | startsWith(String) |
| concat(String) | substring(int,int) |
| copyValueOf(char[]) | toCharArray() |
| endsWith(String) | toLowerCase() |
| equals(Object) | toUpperCase() |
| equalsIgnoreCase(String) | trim() |
| getChars(int,int,char[],int) | valueOf(int) |
| indexOf(String) | valueOf(long) |
| lastIndexOf(String) | valueOf(float) |
| length() | valueOf(double) |
| regionMatches(int,String,int,int) | |
For more information see:
http://www.sdsu.edu/doc/java/java.lang.String.html#_top_
Neither String nor char[] end in the null character like char* in C
char[]
- Array of characters
- Only array operations are supported
String
- Is a class with numerous operations
- Integrated into Java's ~200 classes
- Strings are constant,
- Their values cannot be changed after creation
class CommandLineExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
System.out.println( args.length );
for ( int k = 0; k < args.length; k++ )
{
System.out.println( "Argument " + k + "\t" + args[ k ] );
};
Float secondArgument = Float.valueOf( args[ 1 ] );
System.out.println( secondArgument );
}
}
rohan 16-> java CommandLineExample 1 2 3 4 5
5
Argument 0 1
Argument 1 2
Argument 2 3
Argument 3 4
Argument 4 5
2
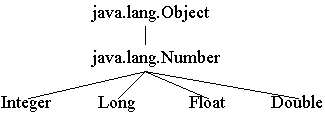
Why Numeric Classes?
- "The numeric classes provide an object wrapper for numeric data values and
serves as a place for numeric-oriented operations. A wrapper is useful because
most of Java's utility classes require the use of objects. Since int, long,
float and double are not objects in Java, they need to be wrapped in a class
instance."
class NumericClassesExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
Integer height = new Integer( 10 );
Integer width = new Integer( 25 );
Integer depth = 25; // Compile error
Integer area;
area = height * width; // Compile error
area = new Integer(height.intValue() * width.intValue() );
System.out.println( area );
String areaAsString = area.toString();
int areaAsInt = area.intValue();
long areaAsLong = area.longValue();
System.out.println( Integer.MAX_VALUE );
}
}
Some (not all) Numeric Operations
| Class | Integer | Long |
| | |
| Variables | MAX_VALUE | MAX_VALUE |
| MIN_VALUE | MIN_VALUE |
| | |
| Constructors | Integer(int) | Long(long) |
| Integer(String) | Long(String) |
| | |
| Methods | doubleValue() | doubleValue() |
| equals(Object) | equals(Object) |
| floatValue() | floatValue() |
| intValue() | intValue() |
| longValue() | longValue() |
| toString() | toString() |
| valueOf(String) | valueOf(String) |
Some (not all) Numeric Operations
| Class | Float | Double |
| | |
| Variables | MAX_VALUE | MAX_VALUE |
| MIN_VALUE | MIN_VALUE |
| NEGATIVE_INFINITY | NEGATIVE_INFINITY |
| NaN | NaN |
| POSITIVE_INFINITY | POSITIVE_INFINITY |
| | |
| Constructors | Float(float) | Double(double) |
| Float(double) | Double(String) |
| Float(String) | |
| | |
| Methods | doubleValue() | doubleValue() |
| equals(Object) | equals(Object) |
| intValue() | floatValue() |
| isInfinite() | intValue() |
| isNaN() | isInfinite() |
| longValue() | isNaN() |
| toString() | longValue() |
| valueOf(String) | toString() |


 CS 596 Client-Server Programming
CS 596 Client-Server Programming CS 596 Client-Server Programming
CS 596 Client-Server Programming